Heat, Internal Energy and Work
Heat, Internal Energy and Work: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as Internal Energy, Work Done by Thermodynamic System, Internal Energy in Thermodynamics and Distinction between Heat and Internal Energy.
Important Questions on Heat, Internal Energy and Work
An ideal is filled in a closed, rigid and thermally-insulated container. A coil of resistance and carrying a current of supplies heaT to the gas. The change in the internal energy of the gas after minutes will be:
For an ideal gas, its internal energy is the function of its:
A gas expands from a volume of to a volume of against an external pressure of . The work done by the gas will be
Calculate the magnitude of work done (in joules) when mole of an ideal gas at expands isothermally and reversibly from an initial volume of litres to the final volume of litres.
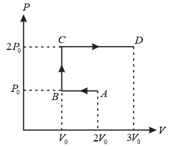
Calculate the work done by an ideal gas in the thermodynamic process depicted in the adjoining graph.
An insulated container containing ideal monoatomic gas of molar mass is moving with a velocity . If the container is suddenly stopped. The change in temperature is
For the reaction (at andatm.)
kJ/mol; will be
If gas expands at constant temperature and pressure, then its
The percentage change in internal energy, when a gas is cooled from to , is
Among the following gases, the one which possesses the largest internal energy is
Which one of the following statements is true, in respect of the usual quantities represented by and
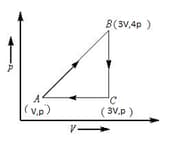
A sample of ideal monoatomic gas is taken around the cycle, as shown in the figure. The work done during the cycle is
Calculate the specific heat capacity Cv of a gaseous mixture consisting of v1 moles of a gas of adiabatic exponent and moles of another gas of adiabatic exponent .
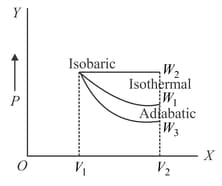
Starting with the same initial conditions, an ideal gas expands from volume to in three different ways. The work done by the gas is if the process is purely isothermal, if purely isobaric and purely adiabatic. Then
1 cm3 of water at its boiling point absorbs 540 cal of heat to become steam with a volume of 1671 cm3. If the atmospheric pressure is 1.013 x 105 N/m2 and the mechanical equivalent of heat = 4.19 J/cal, the energy spent in this process in overcoming intermolecular forces is
represents the ratio of two specific heats of a gas. For a given mass of the gas, the change in internal energy when the volume expands from V to 3V at constant pressure P is
A thermodynamical system is changed from state to by two different processes. The quantity which will remain the same will be
